C# 程序设计 作业和实验 例题 随机数、排序 生成20个不同的随机数,要求利用一维数组来求解问题。利用Random类可生成随机数,每个数在10(含)和100(不含)之间。在生成每个数值时,检查一下是否和之前已存的数一样,如果相同则舍去,不同则存入数组。对这20个各不相同的数排序(使用Array.Sort()方法),最后输出。
Random random = new Random(); int count = 0 ;int [] values = new int [20 ];while (count < 20 ) { int n = random.Next(10 , 100 ); bool contains = values.Contains(n); if (!contains) { values[count] = n; count++; } int index = Array.IndexOf(values, n); if (index < 0 ) { values[count] = n; count++; } } Array.Sort(values); for (int i = 0 ; i < values.Length; i++) { Console.Write($"{values[i]} \t" ); if (i == 9 ) Console.WriteLine(); }
字符串 西绪福斯黑洞也就是所谓的123数字黑洞。数学中的123就跟英语中的ABC一样平凡和简单。然而,按以下运算顺序,就可以观察到这个最简单的数字黑洞的值:
string str = Console.ReadLine();while (true ) { int even = 0 ; int odd = 0 ; int sum = str.Length; foreach (char ch in str) { if ((ch - '0' ) % 2 == 0 ) even++; else odd++; } str = $"{even} {odd} {sum} " ; Console.WriteLine(str); if (Convert.ToInt32(str) == 123 ) break ; }
将 1, 2, …, 9共 9 个数字分成 3 组,分别组成 3 个三位数,且使这 3 个三位数构成1:2:3 的比例,试求出所有满足条件的 3 个三位数。可能要用到字符串的一些方法:IndexOf查询某个字符或子串的位置,找不到返回-1;Contains查询是否包含某个字符或子串;其它方法请查询帮助文件。
static void Main (string [] args for (int a = 101 ; a < 333 ; a++) { string str = a.ToString(); if (str.IndexOf('0' ) > 0 ) continue ; int b = 2 * a; int c = 3 * a; string allchs = $"{a} {b} {c} " ; if (allchs.IndexOf('0' ) > 0 ) continue ; char [] chars = allchs.ToCharArray(); Array.Sort(chars); allchs = new string (chars); if (allchs == "123456789" ) Console.WriteLine($"{a} \t{b} \t{c} " ); if (allchs.Contains('1' ) && allchs.Contains('2' ) && allchs.Contains('3' ) && allchs.Contains('4' ) && allchs.Contains('5' ) && allchs.Contains('6' ) && allchs.Contains('7' ) && allchs.Contains('8' ) && allchs.Contains('9' )) Console.WriteLine($"{a} \t{b} \t{c} " ); } } static bool check (string s bool [] arr = new bool [10 ]; arr[0 ] = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++) { if (arr[s[i] - '0' ]) return false ; arr[s[i] - '0' ] = true ; } return true ; }
复数包含实部和虚部,现要求对字符串”2+3i”进行解析,输出其实部和虚部的值,该方法可定义为:
bool TryParse(string s, out int real, out int image)
提示:可使用double.TryParse(string s, out double value)方法;可使用string的IndexOf(char c)来搜索某个字符在字符串中的位置;可使用string的SubString(int start, int length)来提取子串。
可通过下面程序来测试。
bool ok = TryParse("2+3i" , out double real, out double image);Debug.Assert(ok); Debug.Assert(real == 2 ); Debug.Assert(real == 3 );
(有兴趣的同学可对-2-3i, -3i等复数值进行解析。完整的解析比较复杂,不要求完全解析)。
class Program { static void Main (string [] args double real, image; bool ok = TryParse("2" , out real, out image); Console.WriteLine($"{ok} - {real} : {image} " ); ok = TryParse("-2" , out real, out image); Console.WriteLine($"{ok} - {real} : {image} " ); ok = TryParse("3i" , out real, out image); Console.WriteLine($"{ok} - {real} : {image} " ); ok = TryParse("-3i" , out real, out image); Console.WriteLine($"{ok} - {real} : {image} " ); ok = TryParse("2+3i" , out real, out image); Console.WriteLine($"{ok} - {real} : {image} " ); ok = TryParse("2-3i" , out real, out image); Console.WriteLine($"{ok} - {real} : {image} " ); } public static bool TryParse (string s, out double real, out double image real = 0 ; image = 0 ; if (s == null ) return false ; s.Trim(); bool negativeImage = false ; s = s.ToUpper(); int pos = s.IndexOf('+' ); if (pos < 0 ) { pos = s.IndexOf('-' ); if (pos >= 0 ) negativeImage = true ; } int iPos = s.IndexOf('I' ); if (iPos < 0 ) { if (pos > 0 ) return false ; else return double .TryParse(s, out real); } else { if (pos > 0 ) { string s1 = s.Substring(0 , pos); if (!double .TryParse(s1, out real)) return false ; } string s2 = null ; if (pos < 0 ) { s2 = s.Substring(0 , iPos - pos - 1 ); return double .TryParse(s2, out image); } else { s2 = s.Substring(pos + 1 , iPos - pos - 1 ); if (!double .TryParse(s2, out image)) return false ; image = negativeImage ? -image : image; return true ; } } } }
委托 已有程序框架如下,其中有部分代码缺失,以[—a—]的形式标注。
public delegate bool NumberPredicate (int numberclass Delegates { static void Main (string [] args Random rd = new Random(); int [] numbers = new int [15 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < numbers.Length; i++) numbers[i] = rd.Next(1 , 100 ); Console.WriteLine("原始数组:" ); Array.ForEach(numbers, x => Console.Write($"{x} " )); NumberPredicate evenPredicate = IsEven; Console.WriteLine("利用委托变量evenPredicate判断15是否偶数: {0}" , evenPredicate(15 )); int [] evenNumbers = FilterArray(numbers, evenPredicate); DisplayList("numbers数组中的偶数有 : " , evenNumbers); int [] primeNumbers = FilterArray(numbers, IsPrime); DisplayList("numbers数组中的素数有 : " , primeNumbers); NumberPredicate fiveTimes = x => (x % 5 ) == 0 ; int [] fiveNumbers = FilterArray(numbers, fiveTimes); DisplayList("numbers数组中的5的倍数有 : " , fiveNumbers); } private static int [] FilterArray (int [] intArray, NumberPredicate predicate int size = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < intArray.Length; i++) { if (predicate(intArray[i])) size++; } int [] results = new int [size]; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < intArray.Length; i++) { if (predicate(intArray[i])) results[index++] = intArray[i]; } return results; } private static bool IsEven (int number return (number % 2 == 0 ); } private static bool IsPrime (int number if (number <= 1 ) return false ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= (int )(Math.Sqrt(number)); i++) { if (number % i == 0 ) return false ; } return true ; } private static void DisplayList (string description, int [] list Console.WriteLine(description); foreach (int i in list) { Console.Write($"{i} \t" ); } Console.WriteLine(); } }
类 创建一个Vector类,既可表示一个三维向量,也可表示三维空间的点。它具有以下成员:
class Program { static void Main (string [] args Vector v1 = new Vector(5 , 2 ); Vector v2 = new Vector(2 , 2 , 2 ); Console.WriteLine(v1.Magnitude); Console.WriteLine(v2.Normalized); Console.WriteLine(v1.DistanceTo(v2)); Console.WriteLine(v1.MoveTowards(v2, 2 )); } } class Vector { public const double epsilon = 0.00001 ; private double x, y, z; public static Vector left = new Vector(-1 , 0 , 0 ); public static Vector right = new Vector(0 , 0 , 1 ); public static Vector zero = new Vector(); public double X { get => x; set => x = value ; } public double Y { get => y; set => y = value ; } public double Z { get => z; set => z = value ; } public Vector (double x, double y, double z => (this .x, this .y, this .z) = (x, y, z); public Vector (double x, double ythis (x, y, 0 ) public Vector () : this (0 , 0 , 0 public double Magnitude { get => Math.Sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z); } public Vector Normalized { get { double mag = Magnitude; if (mag > epsilon) return new Vector(x / mag, y / mag, z / mag); else return zero; } } public double DistanceTo (Vector v ) double diff_x = x - v.x; double diff_y = y - v.y; double diff_z = z - v.z; return (float )Math.Sqrt(diff_x * diff_x + diff_y * diff_y + diff_z * diff_z); } public Vector MoveTowards (Vector target, double distance ) Vector direction = new Vector(target.X - x, target.Y - y, target.Z - z); double mag = direction.Magnitude; if (mag < epsilon) return target; return new Vector(x + direction.x * distance / mag, y + direction.y * distance / mag, z + direction.z * distance / mag); } public override string ToString () => $"({x} , {y} , {z} )" ; }
1. 按要求编写代码,并进行代码重构:
创建一个Time类,具有以下成员:
(1)int类型字段hour, minute, second;
(2)int类型属性Hour, Minute, Second,其中,要求在set访问器对用户提供的值进行校验,Hour在0-23之间,Minute和Second均在0-59之间。被赋其它值时抛出异常,抛出方法:
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(value), value,
$”{nameof(Hour)} must be 0 - 23”);
(3)编写无参构造函数和三参构造函数。无参构造函数调用三参构造函数。为参数提供默认值0;
(4)编写Time Next(int hour, int minute, int second)函数,在现有时间上加上参数指定时间段后,返回新的时间信息;
(5)编写string ToUniversalString()方法,输出24时制的时分秒信息;
(6)编写string ToString()方法,加上override修饰,输出12时制的时间信息,并添加AM和PM后缀。
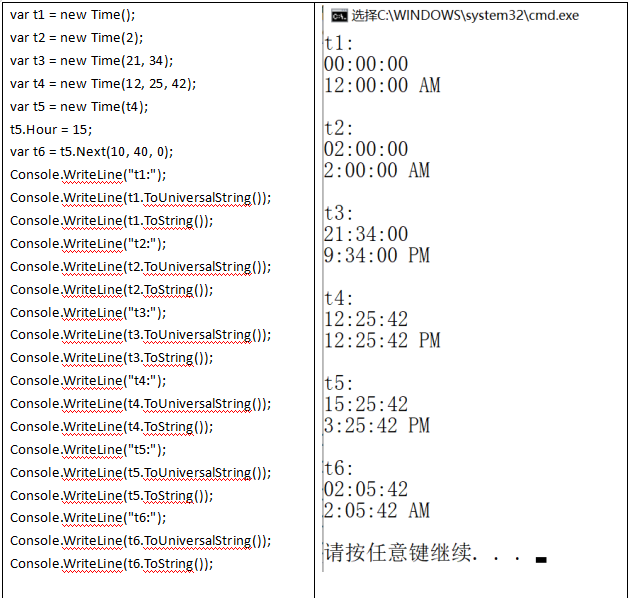
运行以下左侧测试代码,输出结果如右侧所示:
public class Time2 { private int hour; private int minute; private int second; public Time2 (int hour = 0 , int minute = 0 , int second = 0 SetTime(hour, minute, second); } public Time2 (Time2 t ) : this (t.Hour, t.Minute, t.Second ) { } public void SetTime (int hour, int minute, int second Hour = hour; Minute = minute; Second = second; } public Time2 Next (int hour = 0 , int minute = 0 , int second = 0 int seconds = (Hour + hour) * 3600 + (Minute + minute) * 60 + Second + second; Time2 newTime = new Time2(); newTime.Hour = (seconds / 3600 ) % 24 ; newTime.Minute = (seconds % 3600 ) / 60 ; newTime.Second = seconds % 60 ; return newTime; } public int Hour { get { return hour; } set { if (value < 0 || value > 23 ) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof (value ), value , $"{nameof (Hour)} must be 0 - 23" ); } hour = value ; } } public int Minute { get { return minute; } set { if (value < 0 || value > 59 ) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof (value ), value , $"{nameof (Minute)} must be 0 - 59" ); } minute = value ; } } public int Second { get { return second; } set { if (value < 0 || value > 59 ) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof (value ), value , $"{nameof (Second)} must be 0 - 59" ); } second = value ; } } public string ToUniversalString () $"{Hour:D2} :{Minute:D2} :{Second:D2} " ; public override string ToString () $"{((Hour == 0 || Hour == 12 ) ? 12 : Hour % 12 )} :" + $"{Minute:D2} :{Second:D2} {(Hour < 12 ? "AM" : "PM" )} " ; } class Ex4 : Object { public static void Main () var t1 = new Time2(); var t2 = new Time2(2 ); var t3 = new Time2(21 , 34 ); var t4 = new Time2(12 , 25 , 42 ); var t5 = new Time2(t4); t5.Hour = 15 ; var t6 = t5.Next(10 , 40 , 0 ); Console.WriteLine("t1:" ); Console.WriteLine($"{t1.ToUniversalString()} " ); Console.WriteLine($"{t1.ToString()} \n" ); Console.WriteLine("t2:" ); Console.WriteLine($"{t2.ToUniversalString()} " ); Console.WriteLine($"{t2.ToString()} \n" ); Console.WriteLine("t3:" ); Console.WriteLine($"{t3.ToUniversalString()} " ); Console.WriteLine($"{t3.ToString()} \n" ); Console.WriteLine("t4:" ); Console.WriteLine($"{t4.ToUniversalString()} " ); Console.WriteLine($"{t4.ToString()} \n" ); Console.WriteLine("t5:" ); Console.WriteLine($"{t5.ToUniversalString()} " ); Console.WriteLine($"{t5.ToString()} \n" ); Console.WriteLine("t6:" ); Console.WriteLine($"{t6.ToUniversalString()} " ); Console.WriteLine($"{t6.ToString()} \n" ); } }
C#语言提供了较好的封装手段,在访问对象状态时提供了属性语法,这样可以更好地控制各种行为,即便在代码重构时内部实现改变了,也不影响其使用。
现在,要求修改上一题的Time类的内部实现,只保留“秒”字段,表示从午夜0时至今的“秒”数,去除时、分两字段。同时要求,保留所有public的对外公开的接口,且功能不变。
重构之后,采用上一题测试代码,要求输出结果不变。
namespace CA3 { public class Time { private int second; public Time (int hour = 0 , int minute = 0 , int second = 0 SetTime(hour, minute, second); } public Time (Time t ) : this (t.Hour, t.Minute, t.Second ) { } public void SetTime (int hour, int minute, int second Hour = hour; Minute = minute; Second = second; } public Time Next (int hour, int minute, int second Time newTime = new Time(this ); newTime.second += hour * 3600 + minute * 60 + second; newTime.second %= 24 * 3600 ; return newTime; } public int Hour { get { return second / 3600 ; } set { if (value < 0 || value > 23 ) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof (value ), value , $"Hour must be 0 - 23" ); } second += (value - Hour) * 3600 ; } } public int Minute { get { return (second % 3600 ) / 60 ; } set { if (value < 0 || value > 59 ) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof (value ), value , $"Minute must be 0 - 59" ); } second += (value - Minute) * 60 ; } } public int Second { get { return second % 60 ; } set { if (value < 0 || value > 59 ) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof (value ), value , $"Second must be 0 - 59" ); } second += value - Second; } } public string ToUniversalString () $"{Hour:D2} :{Minute:D2} :{Second:D2} " ; public override string ToString () $"{((Hour == 0 || Hour == 12 ) ? 12 : Hour % 12 )} :" + $"{Minute:D2} :{Second:D2} {(Hour < 12 ? "AM" : "PM" )} " ; } class Program { public static void Main () var t1 = new Time(); var t2 = new Time(2 ); var t3 = new Time(21 , 34 ); var t4 = new Time(12 , 25 , 42 ); var t5 = new Time(t4); t5.Hour = 15 ; var t6 = t5.Next(10 , 40 , 0 ); Console.WriteLine("t1:" ); Console.WriteLine(t1.ToUniversalString()); Console.WriteLine(t1.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("t2:" ); Console.WriteLine(t2.ToUniversalString()); Console.WriteLine(t2.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("t3:" ); Console.WriteLine(t3.ToUniversalString()); Console.WriteLine(t3.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("t4:" ); Console.WriteLine(t4.ToUniversalString()); Console.WriteLine(t4.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("t5:" ); Console.WriteLine(t5.ToUniversalString()); Console.WriteLine(t5.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("t6:" ); Console.WriteLine(t6.ToUniversalString()); Console.WriteLine(t6.ToString()); } } }
已提供了Ellipse(椭圆)类的实现,要求写两个版本的“圆”类,一个名为DerivingCircle,与Ellipse是继承关系;一个名为ComposingCircle,与Ellipse是包含关系。两个圆类要求具备以下功能:
ComposingCircle c1 = new ComposingCircle(); c1.Radius = 6 ; DerivingCircle c2 = new DerivingCircle(1 , 1 , 3 ); Console.WriteLine(c1); Console.WriteLine(c2); Console.WriteLine("c1是否包含(1, 1):" + c1.Contains(1 , 1 )); Console.WriteLine("c1是否包含c2:" + c1.Contains(c2)); Console.WriteLine("c1与c2是否有重叠:" + c1.Overlaps(c2));
输出为:包含椭圆的圆:圆心在(0, 0),半径为6 继承椭圆的圆:圆心在(1, 1),半径为3 c1是否包含(1, 1):True c1是否包含c2:True c1与c2是否有重叠:True
using System;using System.Collections;using System.Diagnostics;using static System.Console;namespace ConsoleApp { public interface ICircle { double Radius { get ; set ; } double CenterX { get ; set ; } double CenterY { get ; set ; } double Area { get ; } double Perimeter { get ; } bool Contains (double x, double y bool Contains (ICircle circle ) bool Overlaps (ICircle circle ) } class CircleComparer : IComparer <ICircle > { public string CompareType { get ; set ; } public int Compare (ICircle c1, ICircle c2 ) { if (c1 == null || c2 == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(); switch (CompareType) { case "radius" : return c1.Radius.CompareTo(c2.Radius); case "x" : return c1.CenterX.CompareTo(c2.CenterX); case "y" : return c1.CenterY.CompareTo(c2.CenterY); default : throw new ArgumentException("不支持该比较方式" ); } } } class Ellipse { public double CenterX { get ; set ; } public double CenterY { get ; set ; } protected double radiusLong; public virtual double RadiusLong { get { return radiusLong; } set { if (value < 0 ) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("RadiusLong" , value , "RadiusLong必须赋正值" ); radiusLong = value ; if (radiusShort > 0 && value < radiusShort) { radiusLong = radiusShort; radiusShort = value ; } } } protected double radiusShort; public virtual double RadiusShort { get { return radiusShort; } set { if (value < 0 ) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("RadiusShort" , value , "RadiusShort必须赋正值" ); if (value > radiusLong) { radiusShort = radiusLong; radiusLong = value ; } else { radiusShort = value ; } } } public Ellipse (double cx, double cy, double rx, double ry CenterX = cx; CenterY = cy; RadiusLong = rx; RadiusShort = ry; } public virtual double Area { get { return Math.PI * RadiusLong * RadiusShort; } } public virtual double Perimeter { get { return 2 * Math.PI * RadiusShort + 4 * (RadiusLong - RadiusShort); } } public double DistanceTo (double x, double y return Math.Sqrt((CenterX - x) * (CenterX - x) + (CenterY - y) * (CenterY - y)); } public override string ToString () return $"椭圆:圆心在({CenterX} , {CenterY} ),长短半轴为({RadiusLong} , {RadiusShort} )" ; } } class DerivingCircle : Ellipse , ICircle , IComparable { public double Radius { get { return RadiusLong; } set { RadiusLong = value ; RadiusShort = value ; } } public DerivingCircle () : this (0 , 0 , 1 } public DerivingCircle (double cx, double cy, double r : base (cx, cy, r, r ) { Radius = r; } public override double Area { get { return Math.PI * Radius * Radius; } } public override double Perimeter { get { return 2 * Math.PI * Radius; } } public bool Contains (double x, double y return DistanceTo(x, y) <= Radius; } public bool Contains (ICircle circle ) return DistanceTo(circle.CenterX, circle.CenterY) <= Radius - circle.Radius; } public bool Overlaps (ICircle circle ) return DistanceTo(circle.CenterX, circle.CenterY) <= Radius + circle.Radius; } public bool Extend (double range, out ICircle newCircle if (Radius + range < 0 ) { newCircle = new DerivingCircle(CenterX, CenterY, Radius); return false ; } newCircle = new DerivingCircle(CenterX, CenterY, Radius + range); return true ; } public override string ToString () return $"派生的圆:圆心在({CenterX} , {CenterY} ),半径为{Radius} " ; } public int CompareTo (object obj if (obj == null || !(obj is ICircle)) throw new ArgumentException(); ICircle circle = obj as ICircle; return Radius.CompareTo(circle.Radius); } } class ComposingCircle : ICircle , IComparable <ICircle > { private Ellipse ellipse; public double Radius { get { return ellipse.RadiusLong; } set { ellipse.RadiusLong = value ; ellipse.RadiusShort = value ; } } public double CenterX { get => ellipse.CenterX; set => ellipse.CenterX = value ; } public double CenterY { get => ellipse.CenterY; set => ellipse.CenterY = value ; } public ComposingCircle () : this (0 , 0 , 1 } public ComposingCircle (double cx, double cy, double r ellipse = new Ellipse(cx, cy, r, r); } public double Area { get { return Math.PI * Radius * Radius; } } public double Perimeter { get { return 2 * Math.PI * Radius; } } public bool Contains (double x, double y return ellipse.DistanceTo(x, y) <= Radius; } public bool Contains (ICircle circle ) return ellipse.DistanceTo(circle.CenterX, circle.CenterY) <= Radius - circle.Radius; } public bool Overlaps (ICircle circle ) return ellipse.DistanceTo(circle.CenterX, circle.CenterY) <= Radius + circle.Radius; } public bool Extend (double range, out ICircle newCircle if (Radius + range < 0 ) { newCircle = new DerivingCircle(CenterX, CenterY, Radius); return false ; } newCircle = new DerivingCircle(CenterX, CenterY, Radius + range); return true ; } public override string ToString () return $"包含的圆:圆心在({CenterX} , {CenterY} ),半径为{Radius} " ; } public int CompareTo (ICircle obj ) return Radius.CompareTo(obj.Radius); } } public delegate bool CirclePredicate (ICircle number ) public class Exp3_1 { public static void Main () ComposingCircle c1 = new ComposingCircle(); c1.Radius = 6 ; DerivingCircle c2 = new DerivingCircle(1 , 1 , 3 ); Console.WriteLine(c1); Console.WriteLine(c2); Console.WriteLine("c1是否包含(1, 1):" + c1.Contains(1 , 1 )); Console.WriteLine("c1是否包含c2:" + c1.Contains(c2)); Console.WriteLine("c1与c2是否有重叠:" + c1.Overlaps(c2)); Random rd = new Random(); ICircle[] cirs = new ICircle[10 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { cirs[2 * i] = new ComposingCircle(rd.Next(-100 , 100 ), rd.Next(-100 , 100 ), rd.Next(100 )); cirs[2 * i + 1 ] = new DerivingCircle(rd.Next(-100 , 100 ), rd.Next(-100 , 100 ), rd.Next(100 )); } Console.WriteLine("基于半径进行比较" ); Array.Sort(cirs, new CircleComparer { CompareType = "radius" }); Array.ForEach(cirs, x => Console.WriteLine(x)); Console.WriteLine("基于圆心X坐标进行比较" ); Array.Sort(cirs, new CircleComparer { CompareType = "x" }); Array.ForEach(cirs, x => Console.WriteLine(x)); Console.WriteLine("基于圆心Y坐标进行比较" ); Array.Sort(cirs, new CircleComparer { CompareType = "y" }); Array.ForEach(cirs, x => Console.WriteLine(x)); CirclePredicate predicate = InFirstQuadrant; Console.WriteLine("利用委托变量判断是否位于第一象限: {0}" , predicate(cirs[0 ])); List<ICircle> selected = FilterArray(cirs, predicate); DisplayList("数组中的位于第一象限的圆有: " , selected); selected = FilterArray(cirs, IntersectWithAxis); DisplayList("数组中与坐标轴相交的圆有 : " , selected); } private static List<ICircle> FilterArray (ICircle[] array, CirclePredicate predicate ) List<ICircle> list = new List<ICircle>(); foreach (ICircle c in array) { if (predicate(c)) list.Add(c); } return list; } private static bool InFirstQuadrant (ICircle circle ) return circle.CenterX > circle.Radius && circle.CenterX > circle.Radius; } private static bool IntersectWithAxis (ICircle circle ) return Math.Abs(circle.CenterX) < circle.Radius || Math.Abs(circle.CenterY) < circle.Radius; ; } private static void DisplayList (string description, List<ICircle> list Console.WriteLine(description); foreach (ICircle i in list) { Console.WriteLine(i); } } } }
继承 已有两个接口,IBankAccount接口代表一个银行账户能提供的操作,包括存入、支付、查询余额。ITransferBankAccount接口继承IBankAccount接口,并提供转账功能。public interface IBankAccount { void PayIn (decimal amount bool Withdraw (decimal amount decimal Balance { get ; } } public interface ITransferBankAccount : IBankAccount { bool TransferTo (IBankAccount destination, decimal amount ) }
要求写三个类,按以下方式构建继承体系,并重载ToString方法,输出账户主要信息。
IBankAccount sa = new SaverAccount { Balance = 500 }; sa.PayIn(100 ); sa.Withdraw(550 ); Console.WriteLine(sa); Console.WriteLine(); ITransferBankAccount tba = new TransferBankAccount { Balance = 700 }; tba.TransferTo(sa, 750 ); tba.TransferTo(sa, 200 ); Console.WriteLine(tba); Console.WriteLine(); IBankAccount ca = new CreditAccount { Balance = 100 , Limit = 500 }; ca.Withdraw(300 ); ca.Withdraw(400 ); Console.WriteLine(ca);
解答:
using static System.Console;namespace ConsoleApp5 { public interface IBankAccount { void PayIn (decimal amount bool Withdraw (decimal amount decimal Balance { get ; } } public interface ITransferBankAccount : IBankAccount { bool TransferTo (IBankAccount destination, decimal amount ) } public class SaverAccount : IBankAccount { public void PayIn (decimal amount public virtual bool Withdraw (decimal amount if (Balance >= amount) { Balance -= amount; return true ; } WriteLine("支付失败!" ); return false ; } public decimal Balance { get ; set ; } public override string ToString () $"存款账户:余额 = {Balance,6 :C} " ; } public class TransferBankAccount : SaverAccount , ITransferBankAccount { public bool TransferTo (IBankAccount destination, decimal amount ) bool result = Withdraw(amount); if (result) { destination.PayIn(amount); WriteLine("转账成功!" ); } return result; } public override string ToString () $"转账账户:余额 = {Balance,6 :C} " ; } public class CreditAccount : SaverAccount { public decimal Limit { get ; set ; } public override bool Withdraw (decimal amount if (Balance >= amount) { Balance -= amount; return true ; } else if (Balance + Limit > amount) { Balance -= amount; WriteLine("支付成功,已透支!" ); return true ; } else { WriteLine("超出限额,支付失败!" ); return false ; } } public override string ToString () $"信用卡账户:余额 = {Balance,6 :C} , 透支额度 = {Limit,6 :C} " ; } class Ex4 : Object { public static void Main () IBankAccount sa = new SaverAccount { Balance = 500 }; sa.PayIn(100 ); sa.Withdraw(550 ); WriteLine(sa); WriteLine(); ITransferBankAccount tba = new TransferBankAccount { Balance = 700 }; tba.TransferTo(sa, 750 ); tba.TransferTo(sa, 200 ); WriteLine(tba); WriteLine(); IBankAccount ca = new CreditAccount { Balance = 100 , Limit = 500 }; ca.Withdraw(300 ); ca.Withdraw(400 ); WriteLine(ca); } } }
1. 以下代码模拟一个服务类,Server类实现了服务器的创建逻辑,子类只要在生成实例对象时传递一个端口号即可创建一个监听该端口的服务,该代码意图如下:
(1)通过SimpleServer的构造函数接收端口参数。
(2)子类的构造函数默认调用父类的构造函数。
(3)父类的构造函数调用子类的getPort方法获得端口号。
(4)父类构造函数建立端口监听机制(以Console.WriteLine替代)。
(5)对象创建完毕,服务监听启动,正常运行。
运行该程序,多运行几次,查看输出结果,写出你认为的code 1 – 5的执行顺序,并解释原因。
class Test { public int i = 0 ; static void Main (string [] args Server s = new SimpleServer(1000 ); } } abstract class Server { protected const int DEFAULT_PORT = 40000 ; public Server () int port = getPort(); Console.WriteLine("Port: " + port); } protected abstract int getPort () } class SimpleServer : Server { private int port = 100 ; public SimpleServer (int _port port = _port; } protected override int getPort () return (new Random()).NextDouble() > 0.5 ? port : DEFAULT_PORT; } }
code1: 常量定义,在编译时就执行了。
如果将SimpleServer的port修饰符private修改为public,并在Main方法中加上:
当实例化一个子类时,父类以及子类的变量初始化和构造函数的执行顺序如下:
List 要求模拟string类的部分功能,写一个MyString类,它的部分代码如下所示:
class MyString : IComparable <MyString >{ private List<char > chs; public char this [int index]{ get { ...... } } }
要求添加代码,使得以下测试函数可执行,每个输出操作的结果如注释所示。除了ToString方法外,其余方法实现时不得使用string类的功能。
static void Main (string [] args MyString str1 = new MyString("Hello" ); MyString str2 = new MyString("Hello world" ); Console.WriteLine(str2.Length); Console.WriteLine(str2[6 ]); Console.WriteLine(str1.ToLower()); Console.WriteLine(str1.CompareTo(str2.Substring(0 , 5 ))); Console.WriteLine(str1.CompareTo(str2)); MyString str3 = str1 + new MyString(". Nice to meet you." ); Console.WriteLine(str3); }
解答:
class MyString : IComparable <MyString > { private List<char > chs; public char this [int index] { get { if (index < 0 || index >= Length) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); return chs[index]; } } public MyString () chs = new List<char >(); } public MyString (char [] chars chs = new List<char >(chars); } public MyString (string strthis (str.ToCharArray( )) } public int Length { get => chs.Count; } public MyString Substring (int startIndex, int length if (startIndex < 0 || startIndex >= Length || Length < 0 || startIndex + length >= Length) throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); MyString newStr = new MyString(); for (int i = startIndex; i < startIndex + length; i++) { newStr.chs.Add(chs[i]); } return newStr; } public MyString ToLower () char [] temp = new char [Length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.Count; i++) { temp[i] = Char.ToLower(chs[i]); } return new MyString(temp); } public static MyString operator +(MyString str1, MyString str2) { str1.chs.AddRange(str2.chs); return str1; } public int CompareTo (MyString other ) if (other == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException(); int size = (Length > other.Length) ? other.Length : Length; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.Count; i++) { if (chs[i] > other[i]) return 1 ; else if (chs[i] < other[i]) return -1 ; } if (Length > other.Length) return 1 ; else if (Length < other.Length) return -1 ; else return 0 ; } public override string ToString () return new string (chs.ToArray()); } } class Test { static void Main (string [] args MyString str1 = new MyString("Hello" ); MyString str2 = new MyString("Hello world" ); Console.WriteLine(str2.Length); Console.WriteLine(str2[6 ]); Console.WriteLine(str1.ToLower()); Console.WriteLine(str1.CompareTo(str2.Substring(0 , 5 ))); Console.WriteLine(str1.CompareTo(str2)); MyString str3 = str1 + new MyString(". Nice to meet you." ); Console.WriteLine(str3); } }
.NET基础类库的泛型列表类List已经提供了比较丰富的功能,但相比其它语言中内置的列表数据结构还不够强大。为此,要求创建一个类MyList,继承List,用于存储整数,并提供一些方便的功能,包括: lst),将参数中的列表元素复制过来
class Test { static void Main (string [] args List<int > lst = new List<int >() { 1 , 4 , 9 , 6 , 3 , 5 }; WriteLine(lst); MyList lst1 = new MyList(lst); WriteLine("1: " + lst1); MyList lst2 = lst1 * 2 ; WriteLine("2: " + lst2); MyList lst3 = lst2.SubList(4 , 8 ); WriteLine("3 从4到8: " + lst3); MyList lst4 = lst2.SubList(4 , 8 , 2 ); WriteLine("4 从4到8步长2: " + lst4); MyList lst5 = lst2.SubList(-2 , 1 , -3 ); WriteLine("5 从-2到1步长-3: " + lst5); WriteLine("1比2: " + lst1.CompareTo(lst2)); WriteLine("3比4: " + lst3.CompareTo(lst4)); } }
class MyList : List <int >, IComparable <MyList > { public MyList (List<int > lst ) if (lst != null ) AddRange(lst); } public static MyList operator +(MyList left, MyList right) { MyList list = new MyList(left); list.AddRange(right); return list; } public static MyList operator *(MyList left, int numOfCopies) { MyList list = new MyList(left); while (numOfCopies != 1 ) { list.AddRange(left); numOfCopies--; } return list; } public MyList SubList (int start, int stop = 0 , int step = 1 if (start < 0 ) start = Count + start; if (stop < 0 ) stop = Count + stop; if (step == 0 ) throw new ArgumentException("step不可为负数" ); MyList result = new MyList(null ); if (step > 0 ) { for (int i = start; i < stop; i += step) { result.Add(this [i]); } } else { for (int i = start; i > stop; i += step) { result.Add(this [i]); } } return result; } public override string ToString () StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder("[" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < Count; i++) { result.Append(this [i]); if (i != Count - 1 ) result.Append(", " ); } result.Append("]" ); return result.ToString(); } public int CompareTo (MyList? other ) if (other == null ) throw new ArgumentNullException("Argument null in CompareTo" ); int size = (Count < other.Count) ? Count : other.Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { if (this [i] != other[i]) return this [i] - other[i]; } return Count - other.Count; } } class Ex4 : Object { public static void Main () List<int > lst = new List<int >() { 1 , 4 , 9 , 6 , 3 , 5 }; WriteLine(lst); MyList lst1 = new MyList(lst); WriteLine("1: " + lst1); MyList lst2 = lst1 * 2 ; WriteLine("2: " + lst2); MyList lst3 = lst2.SubList(4 , 8 ); WriteLine("3 从4到8: " + lst3); MyList lst4 = lst2.SubList(4 , 8 , 2 ); WriteLine("4 从4到8步长2: " + lst4); MyList lst5 = lst2.SubList(-2 , 1 , -3 ); WriteLine("5 从-2到1步长-3: " + lst5); WriteLine("1比2: " + lst1.CompareTo(lst2)); WriteLine("3比4: " + lst3.CompareTo(lst4)); } }
LINQ 编写一个控制台程序:List<char>中。(可使用Random类和它的Next(int MaxValue)方法)wzzlesgurcpoupisragrejogivpnydacdegijlnoprsuvwyz
List<char > lst = new List<char >(30 ); Random rd = new Random(); WriteLine("原字母:" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++) { lst.Add((char )('a' + rd.Next(26 ))); Console.Write(lst[i]); } WriteLine(); var result = from c in lst orderby c select c; WriteLine("查询结果:" ); foreach (var c in result.Distinct()) { Console.Write(c); }
矩阵数组 矩阵求和:
1)写一个方法,可对两个矩阵求和。方法定义如下:
double[,] AddMatrix(double[,] a, double[,] b)
方法首先要判断矩阵的维度是一样的。假设和为矩阵c,则cij = aij + bij。
2)写一个测试程序,要求用户输入行数和列数,据此随机生成矩阵中的数据,将矩阵相加后输出结果。
3)样例如下:
请输入矩阵行数:2 请输入矩阵列数:3 矩阵加法: 7 7 6| 7 0 1| 14 7 7 8 5 5| 9 8 4| 17 13 9
using static System.Console;class Ex4 { static void Main (string [] args Write("请输入矩阵行数:" ); int row = int .Parse(ReadLine()); Write("请输入矩阵列数:" ); int col = int .Parse(ReadLine()); double [,] arr1 = new double [row, col]; double [,] arr2 = new double [row, col]; Random rd = new Random(); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; j++) { arr1[i, j] = rd.Next(10 ); arr2[i, j] = rd.Next(10 ); } } Console.WriteLine("矩阵加法:" ); double [,] result = AddMatrix(arr1, arr2); for (int i = 0 ; i < result.GetLength(0 ); i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < result.GetLength(1 ); j++) { Console.Write($"{arr1[i, j],4 } " ); } Console.Write("|\t" ); for (int j = 0 ; j < result.GetLength(1 ); j++) { Console.Write($"{arr2[i, j],4 } " ); } Console.Write("|" + "\t" ); for (int j = 0 ; j < result.GetLength(1 ); j++) { Console.Write($"{result[i, j],4 } " ); } Console.WriteLine(); } } public static double [,] AddMatrix(double [,] a, double [,] b) { if (a.GetLength(0 ) != b.GetLength(0 ) || a.GetLength(1 ) != b.GetLength(1 )) return null ; int n = a.GetLength(0 ); int m = a.GetLength(1 ); double [,] result = new double [n, m]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++) { result[i, j] = a[i, j] + b[i, j]; } } return result; } }
参数修饰符 ref和out都是C#中的参数修饰符,它们允许方法修改调用方传递的变量值。尽管它们有相似之处,但它们之间还是存在一些关键区别:
初始化要求:
ref:在将变量传递给带有ref参数的方法之前,必须对变量进行初始化。这意味着变量必须有一个值。out:在将变量传递给带有out参数的方法之前,不需要对变量进行初始化。这意味着变量可以没有值。
方法内赋值要求:
ref:对于ref参数,方法可以选择是否修改参数的值。也就是说,方法内部不一定要为ref参数赋值。out:对于out参数,方法必须在返回之前为其赋值。否则,编译器会报错。
params修饰符在C#中用于表示一个方法可以接受可变数量的参数。它通常用于方法参数列表的最后一个参数,并且参数类型必须是数组。当调用带有params修饰符的方法时,可以传入任意数量的参数,这些参数将被组合成一个数组。这使得方法调用更加灵活,因为你不需要为不同数量的参数创建多个重载版本。
下面是一个使用params修饰符的示例:
using System;class Program { static void Main (string [] args { Console.WriteLine("Sum of 1, 2, 3: " + Sum(1 , 2 , 3 )); Console.WriteLine("Sum of 4, 5: " + Sum(4 , 5 )); Console.WriteLine("Sum of 6: " + Sum(6 )); Console.WriteLine("Sum of no numbers: " + Sum()); } public static int Sum (params int [] numbers { int sum = 0 ; foreach (int number in numbers) { sum += number; } return sum; } }
在这个示例中,我们定义了一个名为Sum的方法,它使用params修饰符接受一个int类型的可变参数数组。在方法内部,我们遍历数组中的所有元素并计算它们的和。在Main方法中,我们展示了如何调用Sum方法,传入不同数量的参数。注意,我们不需要创建多个Sum方法的重载版本来处理不同数量的参数,因为params修饰符允许我们传入任意数量的参数。
设计一个工具类,包含四个函数:
函数一:输入3个参数值,返回其算术平均值
函数二:输入3个参数值,使用ref参数,输出最大值、最小值、平均值。
函数三,输入3个参数值,使用out参数,同样输出最大值、最小值、平均值。
函数四,输入n个参数,采用元组返回最大值、最小值、平均值。
在主函数中进行测试。
class MeanTool { public static double Mean (double a, double b, double c return …; } …… } class Program { public static void Main () double value1 = 2.0 , ……; Console.WriteLine("函数1:{0}" , MeanTool.Mean(value1, ……)); double result1 = 0.0 ; …… } }
class MeanTool { public static double Mean (double a, double b, double c return (a + b + c) / 3 ; } public static void Mean (double a, double b, double c, ref double max, ref double min, ref double average ) max = min = a; max = (max > b) ? max : b; min = (min < b) ? min : b; max = (max > c) ? max : c; min = (min < c) ? min : c; average = (a + b + c) / 3 ; } public static void Mean2 (double a, double b, double c, out double max, out double min, out double average ) max = min = a; max = (max > b) ? max : b; min = (min < b) ? min : b; max = (max > c) ? max : c; min = (min < c) ? min : c; average = (a + b + c) / 3 ; } public static (double , double , double Mean (params double [] numbers double max = 0 ; double min = 0 ; double average = 0 ; if (numbers.Length == 0 ) return (0 , 0 , 0 ); max = numbers[0 ]; min = numbers[0 ]; double sum = numbers[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < numbers.Length; i++) { if (numbers[i] > max) max = numbers[i]; if (numbers[i] < min) min = numbers[i]; sum += numbers[i]; } average = sum / numbers.Length; return (max, min, average); } } class Ex3 { public static void Main () double max = 2 , min = 3 , average = 4 ; Console.WriteLine($"函数1:(2, 3, 4) -> {MeanTool.Mean(max, min, average)} " ); Console.Write("函数2:" ); MeanTool.Mean(2 , 3 , 4 , ref max, ref min, ref average); Console.WriteLine($"(2, 3, 4) -> ({max} , {min} , {average} )" ); Console.Write("函数3:" ); MeanTool.Mean2(12 , 3 , 9 , out max, out min, out average); Console.WriteLine($"(12, 3, 9) -> ({max} , {min} , {average} )" ); Console.Write("函数4:" ); (max, min, average) = MeanTool.Mean(2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ); Console.WriteLine($"(2, 3, 4, 5, 6) -> ({max} , {min} , {average} )" ); } }
值类型 引用类型 struct SomeVal { public int x; }class SomeRef { public int x; }class SomeRef2 { public SomeVal val; }struct SomeVal3 { public SomeRef rf; }class Program { public static void Main () SomeVal v1; v1.x = 100 ; Console.WriteLine(v1.x); v1 = new SomeVal(); Console.WriteLine(v1.x); v1.x = 5 ; Console.WriteLine(v1.x); SomeRef r1; r1 = new SomeRef(); Console.WriteLine(r1.x); r1.x = 5 ; Console.WriteLine(r1.x); SomeVal v2 = v1; SomeRef r2 = r1; v1.x = 9 ; r1.x = 8 ; Console.WriteLine(r1.x); Console.WriteLine(r2.x); Console.WriteLine(v1.x); Console.WriteLine(v2.x); SomeRef2 sf2_1 = new SomeRef2(); SomeVal sv2_1 = sf2_1.val; SomeRef2 sf2_2 = new SomeRef2(); SomeVal sv2_2 = sf2_2.val; Console.WriteLine($"两个类实例相等吗?{sf2_1.Equals(sf2_2)} " ); Console.WriteLine($"两个结构实例相等吗?{sv2_1.Equals(sv2_2)} " ); SomeVal3 sv3_1 = new SomeVal3(); SomeVal3 sv3_2 = new SomeVal3(); Console.WriteLine($"{sv3_1.rf == null } {sv3_2.rf == null } " ); Console.WriteLine($"两个结构实例相等吗?{sv3_1.Equals(sv3_2)} " ); sv3_1.rf = new SomeRef(); sv3_2.rf = new SomeRef(); Console.WriteLine($"两个类实例相等吗?{sv3_1.rf.Equals(sv3_2.rf)} " ); } }
Lambda 按要求编写Lambda表达式:
.NET已定义的Func<out TResult>是一个泛型委托,它封装一个方法,该方法不具有参数,且返回由 TResult 参数指定的类型的值。它的使用,举一例如下:
Func<int > f1 = () => DateTime.Now.Year; Console.WriteLine(f1());
该泛型委托有好几个同名兄弟类型,如Func,Func 等(直到T16)等,仿照上面的例子编写Lambda表达式,并调用它们:
(1)写一个Lambda表达式赋给Func f2,使其完成取平方根功能(可用Math.Sqrt方法)。
(2)写一个Lambda表达式赋给Func f3,使两个整数参数先平方,再相加,再取平方根。
(3)Predicate<T>泛型委托代表一类函数,它们对参数实施判断并返回bool值,实际上表示一种条件。写一个Predicate<int>型Lambda表达式,并调用它。
(4)Action、Action<T>、Action…等委托封装的方法,有0至16个参数,但没有返回值,试写出Action<String>和Action<int, List<int>>的Labmda表达式,并调用它们。
(调用它们时,如果需要参数,则自行生成;可以和Java中的Lambda表达式比较一下)
Func<int , double > f2 = x => Math.Sqrt(x); Console.WriteLine(f2(3 )); Func<int , int , double > f3 = (x, y) => Math.Sqrt(x * x + y * y); Console.WriteLine(f3(3 , 4 )); int num = 5 ;Predicate<int > modn = x => x % num == 0 ; Console.WriteLine($"-3 is {num} 's multiple? {modn(-3 )} " ); Action<string > print = name => Console.Write(name + "\t" ); print("Hello" ); print("World" ); Console.WriteLine(); Action<int , List<int >> a2 = (x, y) => y.Add(x); List<int > lst = new List<int >(); a2(1 , lst); a2(2 , lst); foreach (int value in lst) Console.WriteLine(value );
IComparable IComparer IComparable和IComparer都是在C#中用于比较对象的接口,但它们的使用方式和目的有所不同。
IComparable<T>接口用于让一个类或结构体的实例可以与其他实例进行比较。实现此接口的类需要定义一个CompareTo方法,该方法返回一个整数,表示两个实例的相对顺序。如果实例等于传入的对象,则返回0;如果实例小于传入的对象,则返回负数;如果实例大于传入的对象,则返回正数。
IComparer<T>接口用于定义一个比较器,它可以比较两个对象的相对顺序。实现此接口的类需要定义一个Compare方法,该方法接受两个参数,表示要比较的对象。Compare方法的返回值与IComparable<T>的CompareTo方法相同。
下面是一个简单的代码示例,展示了如何使用这两个接口:
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;public class Person : IComparable <Person >{ public string Name { get ; set ; } public int Age { get ; set ; } public int CompareTo (Person other ) if (other == null ) return 1 ; return Age.CompareTo(other.Age); } } public class PersonComparer : IComparer <Person >{ public int Compare (Person x, Person y ) if (x == null ) return y == null ? 0 : -1 ; if (y == null ) return 1 ; return x.Name.CompareTo(y.Name); } } public class Program { public static void Main () List<Person> people = new List<Person>{ new Person { Name = "Alice" , Age = 30 }, new Person { Name = "Bob" , Age = 25 }, new Person { Name = "Charlie" , Age = 35 } }; people.Sort(); Console.WriteLine("Sorted by age:" ); foreach (var person in people){ Console.WriteLine($"{person.Name} , {person.Age} " ); } people.Sort(new PersonComparer()); Console.WriteLine("\nSorted by name:" ); foreach (var person in people){ Console.WriteLine($"{person.Name} , {person.Age} " ); } } }
这个例子中,Person类实现了IComparable<Person>接口,以便可以根据年龄对Person实例进行排序。PersonComparer类实现了IComparer<Person>接口,用于根据姓名对Person实例进行排序。在Main方法中,我们创建了一个包含三个Person实例的列表,并分别使用IComparable<T>和IComparer<T>接口对其进行排序。
方法重载 方法重载(Method Overloading)是指在同一个类中,允许存在多个具有相同名称但参数列表不同的方法。这些方法在功能上通常是相关的,但是处理不同类型或数量的参数。方法重载是一种多态性(Polymorphism)的表现,它允许程序员使用一个方法名来表示多个功能,使得代码更加简洁易读。
方法重载的规则:
方法名必须相同。
参数列表必须不同,可以是参数数量、参数类型或参数顺序的不同。
返回类型可以相同或不同,但仅仅返回类型的不同不构成重载 。
重载方法可以具有不同的访问修饰符(如public、private等)。仅仅具有不同的访问修饰符不构成重载
以下是C#中的一个简单方法重载示例:
class Calculator { public int Add (int a, int b return a + b; } public double Add (double a, double b return a + b; } public int Add (int a, int b, int c return a + b + c; } }
在这个例子中,Add方法被重载了三次,分别处理两个整数相加、两个浮点数相加和三个整数相加的情况。当你调用Add方法时,C#编译器会根据传递的参数类型和数量自动选择合适的重载方法。
常用容器 C#中常用的容器主要来自于System.Collections和System.Collections.Generic命名空间。以下是一些常用的容器:
1. List<T>:表示可调整大小的动态数组,用于存储同一类型的对象。 2. Dictionary<TKey, TValue>:表示键值对的集合,它允许你通过键来访问值。这是一个哈希表实现。 3. HashSet<T>:表示一组不包含重复元素的集合,它提供了高性能的集合操作,如插入、删除和查找。 4. Stack<T>:表示一个后进先出(LIFO)的对象集合,可以用于存储和检索对象。 5. Queue<T>:表示一个先进先出(FIFO)的对象集合,用于存储和检索对象。 6. LinkedList<T>:表示一个双向链表,它提供了在链表中插入和删除节点的高效操作。 7. SortedList<TKey, TValue>:表示根据键排序的键值对的集合。它允许你通过键来访问值。 8. SortedSet<T>:表示一组不包含重复元素的集合,元素按排序顺序存储。 9. SortedDictionary<TKey, TValue>:表示根据键排序的键值对的集合,它允许你通过键来访问值。
这些容器大多数都有泛型和非泛型版本。泛型容器(如List<T>)允许你指定元素的类型,从而提供类型安全和性能优势。非泛型容器(如ArrayList)则可以存储任何类型的对象,但可能需要进行类型转换和装箱/拆箱操作。在实际编程中,推荐使用泛型容器。
System.Collections 和 System.Collections.Generic 是 C# 中两个不同的命名空间,它们都包含了一组用于存储和操作数据的容器。这两个命名空间的主要区别在于容器的类型安全性和性能。
System.Collections:这个命名空间包含了非泛型容器,例如 ArrayList、Hashtable 和 Stack 等。非泛型容器可以存储任意类型的对象,但在使用时可能需要进行类型转换和装箱/拆箱操作。这可能导致运行时错误(例如类型转换错误)和性能损失。此外,由于缺乏类型约束,代码可读性和维护性也可能受到影响。
System.Collections.Generic:这个命名空间包含了泛型容器,例如 List<T>、Dictionary<TKey, TValue> 和 HashSet<T> 等。泛型容器允许你指定容器中元素的类型,从而提供了类型安全性。这意味着编译器在编译时会检查类型,减少了运行时错误的可能性。泛型容器还提供了更好的性能,因为它们避免了装箱/拆箱操作和不必要的类型转换。泛型容器还提高了代码的可读性和维护性,因为它们明确指定了容器中元素的类型。
总之,System.Collections 和 System.Collections.Generic 的主要区别在于类型安全性和性能。在实际编程中,推荐使用 System.Collections.Generic 中的泛型容器,因为它们提供了更好的类型安全性和性能。