编译原理 SLR(1) 语法分析器的构建 实验三 自底向上语法分析器的构建 项目代码:https://github.com/chen2438/zstu-study/tree/main/%E7%BC%96%E8%AF%91%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86/%E5%AE%9E%E9%AA%8C/%E5%AE%9E%E9%AA%8C%E4%B8%89/
一、 实验要求 运用SLR(1)或者LR(1)分析法,针对给定的上下文无关文法,给出实验方案。预估实验中可能出现的问题。
二、 实验方案 (评价依据实验方案设计是否合理,包括输入输出的设计)
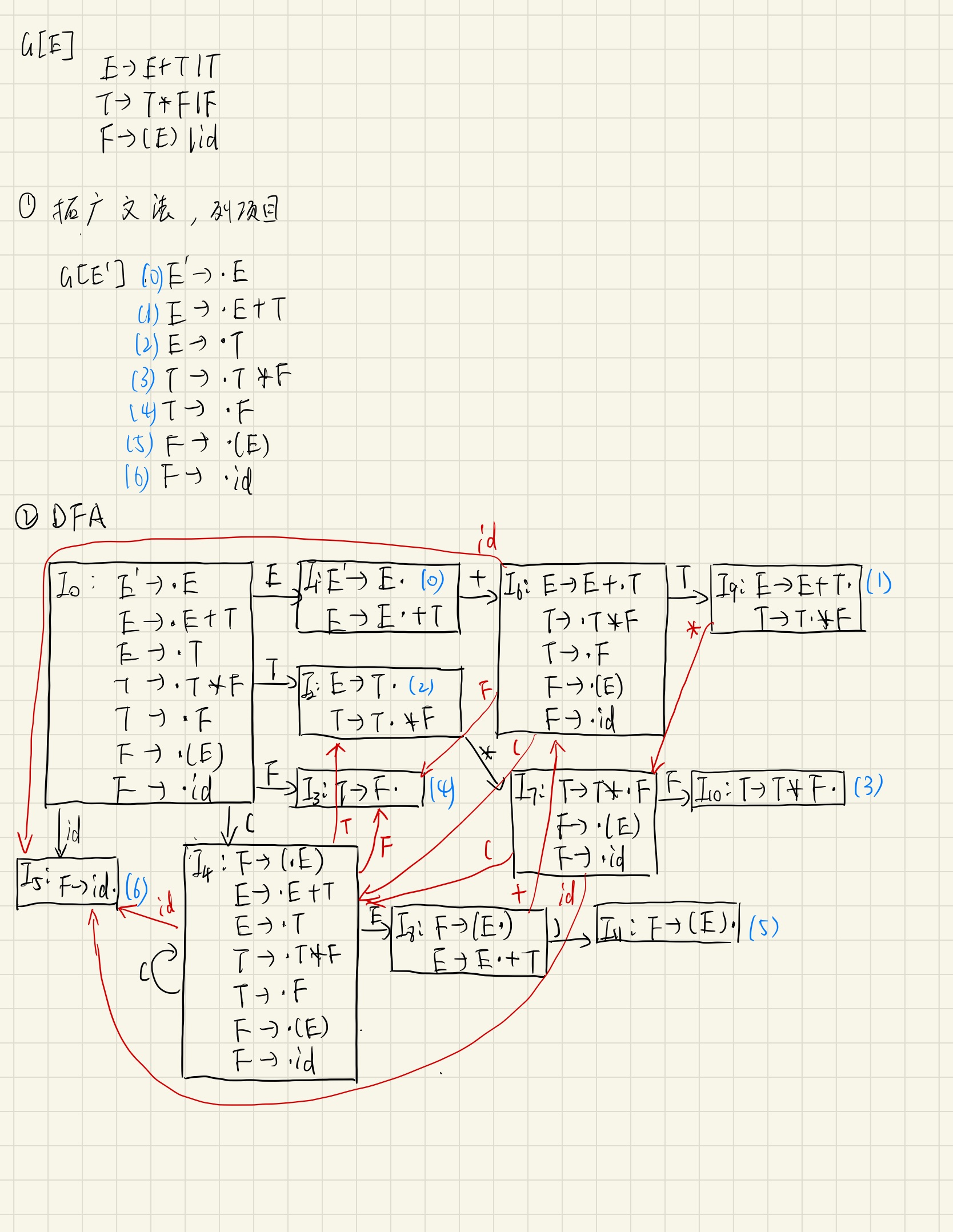
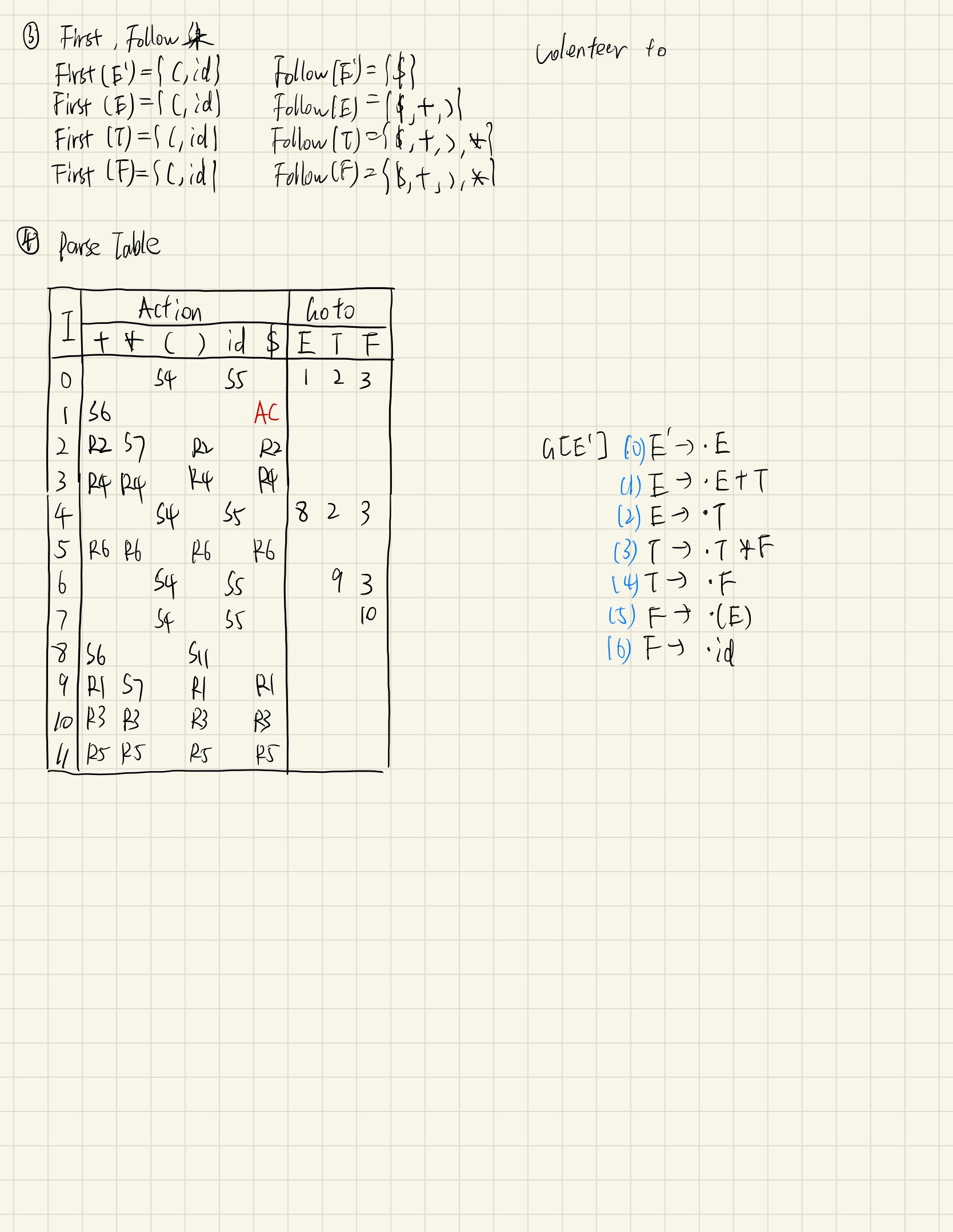
使用SLR(1)文法。逐步完成Augmented Grammar、First&Follow Set、DFA、Parse Table。
然后将分析表处理为程序可读数据,程序根据分析表的内容得出分析过程和结果。
输入设计:
Parse Table、Augmented Grammar。
输出设计:
带有Parsing Stack、Input和Action的分析过程。
三、 预估问题 (是否有预估的问题,预估的问题是否合理)
程序需要事先获得Augmented Grammar、Parse Table、Terminals、Non-terminals的具体内容,这些数据都要被处理为适当的格式,过程比较繁琐。
可以将每个(non)terminal映射为数字,便于直接调用table(i,(non)terminal)。
注意非终结符id的特殊处理。
理论基础 (评价依据 理论知识非常清楚)
四、 内容和步骤 1、考虑简单算术表达式文法G: E→E + T | T T→T * F | F F→(E) | id
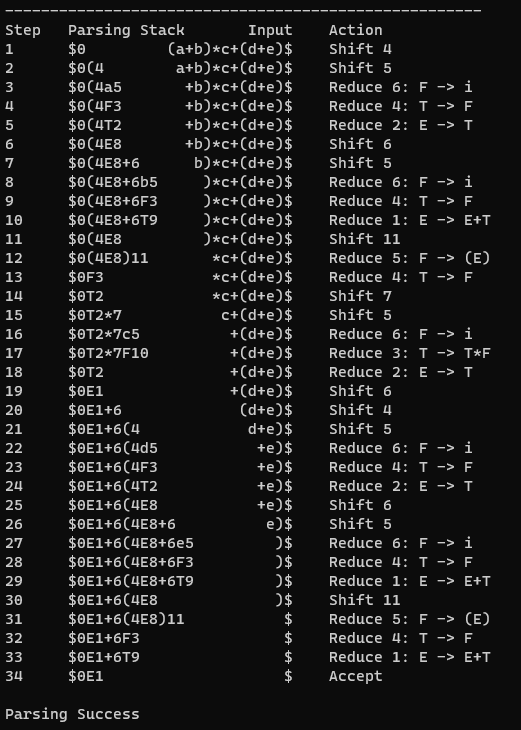
试设计SLR(1)或者LR(1)分析程序,以输入的 (a+b)*c+(d+e) 符号串进行语法分析。
2、实验具体步骤
输入数据:
五、 实验结果: 1、 代码 #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <stack> #include <string> using namespace std;int table[20 ][20 ][2 ];int mp[200 ];string terminals = "+*()i$ETF" ; string inputString = "(a+b)*c+(d+e)" ; stack<int > pStk, iStk; stack<int > reduceResult; string reduce[7 ][2 ]; int step = 1 ;namespace Graph { const int N = 1000 , M = N * 2 ; int nodemap[N] = { 0 , 'E' }; int depth[N]; struct Edge { int to, nxt; }e[M]; int adt, head[N]; void add (int u, int v) e[++adt] = { v,head[u] }; head[u] = adt; } int fa[N]; void dfs (int p1) for (int i = 0 ; i < depth[p1]; i++) { cout << " |" ; } cout << "--" << (char )nodemap[p1] << endl; for (int i = head[p1]; i != 0 ; i = e[i].nxt) { int p2 = e[i].to; if (p2 == fa[p1]) continue ; fa[p2] = p1; dfs (p2); } } void parseTree () int vst[1000 ] = { 0 }; depth[1 ] = 0 ; int cnt = 2 ; while (!reduceResult.empty ()) { int rTop = reduceResult.top (); reduceResult.pop (); int leftChar = reduce[rTop][0 ][0 ]; string rightString = reduce[rTop][1 ]; int oldCnt = cnt; for (int j = oldCnt - 1 ; j >= 1 ; j--) { if (nodemap[j] == leftChar and !vst[j]) { vst[j] = 1 ; for (char k : rightString) { nodemap[cnt] = k; depth[cnt] = depth[j] + 1 ; add (j, cnt); cnt++; } break ; } } } dfs (1 ); } } stack<int > reverse (stack<int > s) { stack<int > tmp; while (!s.empty ()) { tmp.push (s.top ()); s.pop (); } s = tmp; return s; } string reverse (string s) { reverse (s.begin (), s.end ()); return s; } void show (stack<int > ps, stack<int > is) ps = reverse (ps); int width = 25 ; string str1, str2; int odd = 1 ; while (!ps.empty ()) { if (odd == 1 ) str1 += (char )ps.top (); else str1 += to_string (ps.top ()); odd *= -1 ; ps.pop (); } while (!is.empty ()) { str2 += (char )is.top (); is.pop (); } string strBlank (width - str1.size() - str2.size(), ' ' ) ; cout << str1 << strBlank << str2; } void init () for (int i = 0 ; i < terminals.size (); i++) { mp[terminals[i]] = i; if (terminals[i] == 'i' ) { for (int j = 'a' ; j <= 'z' ; j++) { mp[j] = i; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i <= 11 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < terminals.size (); j++) { char c; cin >> c; table[i][j][0 ] = c; } } for (int i = 0 ; i <= 11 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < terminals.size (); j++) { int num; cin >> num; table[i][j][1 ] = num; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < 7 ; i++) { cin >> reduce[i][0 ] >> reduce[i][1 ]; reduce[i][1 ] = reverse (reduce[i][1 ]); } } int parseTable () pStk.push ('$' ); pStk.push (0 ); iStk.push ('$' ); for (int i = inputString.size () - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { iStk.push (inputString[i]); } cout << "---------------------------" << "--------------------------" << endl; cout << "Step Parsing Stack Input Action" << endl; while (!iStk.empty () and !pStk.empty ()) { cout << step << " " ; if (step++ < 10 ) putchar (' ' ); show (pStk, iStk); int pTop = pStk.top (), iTop = iStk.top (); int action[2 ] = { table[pTop][mp[iTop]][0 ], table[pTop][mp[iTop]][1 ] }; if (action[0 ] == 'A' ) { cout << " Accept" << endl; return 200 ; } else if (action[0 ] == 'S' ) { cout << " Shift " << action[1 ] << endl; pStk.push (iTop); pStk.push (action[1 ]); iStk.pop (); } else if (action[0 ] == 'R' ) { reduceResult.push (action[1 ]); cout << " Reduce " << action[1 ] << ": " + reduce[action[1 ]][0 ] + " -> " << reverse (reduce[action[1 ]][1 ]) << endl; for (auto i : reduce[action[1 ]][1 ]) { while (!pStk.empty ()) { int c = pStk.top (); pStk.pop (); if (c == i) break ; if (i == 'i' ) { if ('a' <= c && c <= 'z' ) break ; } } } int pTop1 = pStk.top (); pStk.push (reduce[action[1 ]][0 ][0 ]); int pTop2 = pStk.top (); pStk.push (table[pTop1][mp[pTop2]][1 ]); } else { return 500 ; } } return 500 ; } void solve () init (); int res = parseTable (); if (res == 200 ) { puts ("\nParsing Success" ); } else { puts ("\nParsing Failed" ); } puts ("\nParsing Tree:" ); Graph::parseTree (); } int main () FILE* fp; freopen_s (&fp, "input.txt" , "r" , stdin); solve (); fclose (fp); }
input.txt 放在程序同目录下
n n S n S n Y Y Y S n n n n A n n n R S n R n R n n n R R n R n R n n n n n S n S n Y Y Y R R n R n R n n n n n S n S n n Y Y n n S n S n n n Y S n n S n n n n n R S n R n R n n n R R n R n R n n n R R n R n R n n n 0 0 4 0 5 0 1 2 3 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 7 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 4 4 0 4 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 5 0 8 2 3 6 6 0 6 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 5 0 0 9 3 0 0 4 0 5 0 0 0 10 6 0 0 11 0 0 0 0 0 1 7 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 3 3 0 3 0 3 0 0 0 5 5 0 5 0 5 0 0 0 E' E E E+T E T T T*F T F F (E) F i
2、 截图
六、 实验结论: 1 、实验结论 (是否能够准确描述实验的结论)
本实验使用SLR(1)文法,根据给定上下文无关文法,完成它的分析程序,并在结果中给出分析过程。
程序可以处理给定token序列不满足给定文法的情况。
此程序的优势是可以快速地修改以适用于不同的SLR(1)文法。
2、分析和总结 1)对输入设计的结论
Augmented Grammar使用string reduce[7][2];存储用于规约。
Parse Table使用int table[20][20][2];存储。分两次读入。
Terminals、Non-terminals直接硬编码到代码中。
2)对输出设计的结论
注意输出格式、栈的展示方向、数据左右对齐。
输出分析树时,先根据规约结果生成分析树存到邻接表中,然后DFS遍历整张图并输出。
3)对SLR(1)或者LR(1)分析法的结论
LR(0):见到First集就移进,见到终态就归约
SLR(1)见到First集就移进,见到终态先看Follow集,与Follow集对应的项目归约,其它报错。
SLR分析法包含的展望信息是体现在利用了Follow(A)信息,可以解决“归约-归约”冲突
SLR分析法没有包含足够的展望信息,不能完成解决“移进-归约”冲突,需要改进。
LALR同心集合并不会产生“移进-归约”冲突 ,但会产生“归约-归约”冲突
3、 对预估问题的结论
程序需要事先获得Augmented Grammar、Parse Table、Terminals、Non-terminals的具体内容,这些数据都要被处理为适当的格式,过程比较繁琐。
Augmented Grammar使用string reduce[7][2];存储用于规约。
Parse Table使用int table[20][20][2];存储。分两次读入。
Terminals、Non-terminals直接硬编码到代码中。
可以将每个(non)terminal映射为数字,便于直接调用table(i,(non)terminal)。
注意非终结符id的特殊处理。
以下代码解决2、3问题
for (int i = 0 ; i < terminals.size (); i++) { mp[terminals[i]] = i; if (terminals[i] == 'i' ) { for (int j = 'a' ; j <= 'z' ; j++) { mp[j] = i; } } }
在问题3处,还需注意规约时的字符替换处理。